 Bacteria are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats.
Bacteria are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Although bacterial cells are much smaller and simpler in structure than eukaryotic cells, the bacteria are an exceedingly diverse group of organisms that differ in size, shape, habitat, and metabolism.
Although bacterial cells are much smaller and simpler in structure than eukaryotic cells, the bacteria are an exceedingly diverse group of organisms that differ in size, shape, habitat, and metabolism. In 1838, the German naturalist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg called them ‘bacteria’, from the Greek word ‘baktḗria’, meaning ‘little stick’. Later, Robert Koch’s research, famously dubbed ‘Koch’s postulates’, demonstrated that microorganisms such as bacteria cause infectious diseases.
In 1838, the German naturalist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg called them ‘bacteria’, from the Greek word ‘baktḗria’, meaning ‘little stick’. Later, Robert Koch’s research, famously dubbed ‘Koch’s postulates’, demonstrated that microorganisms such as bacteria cause infectious diseases.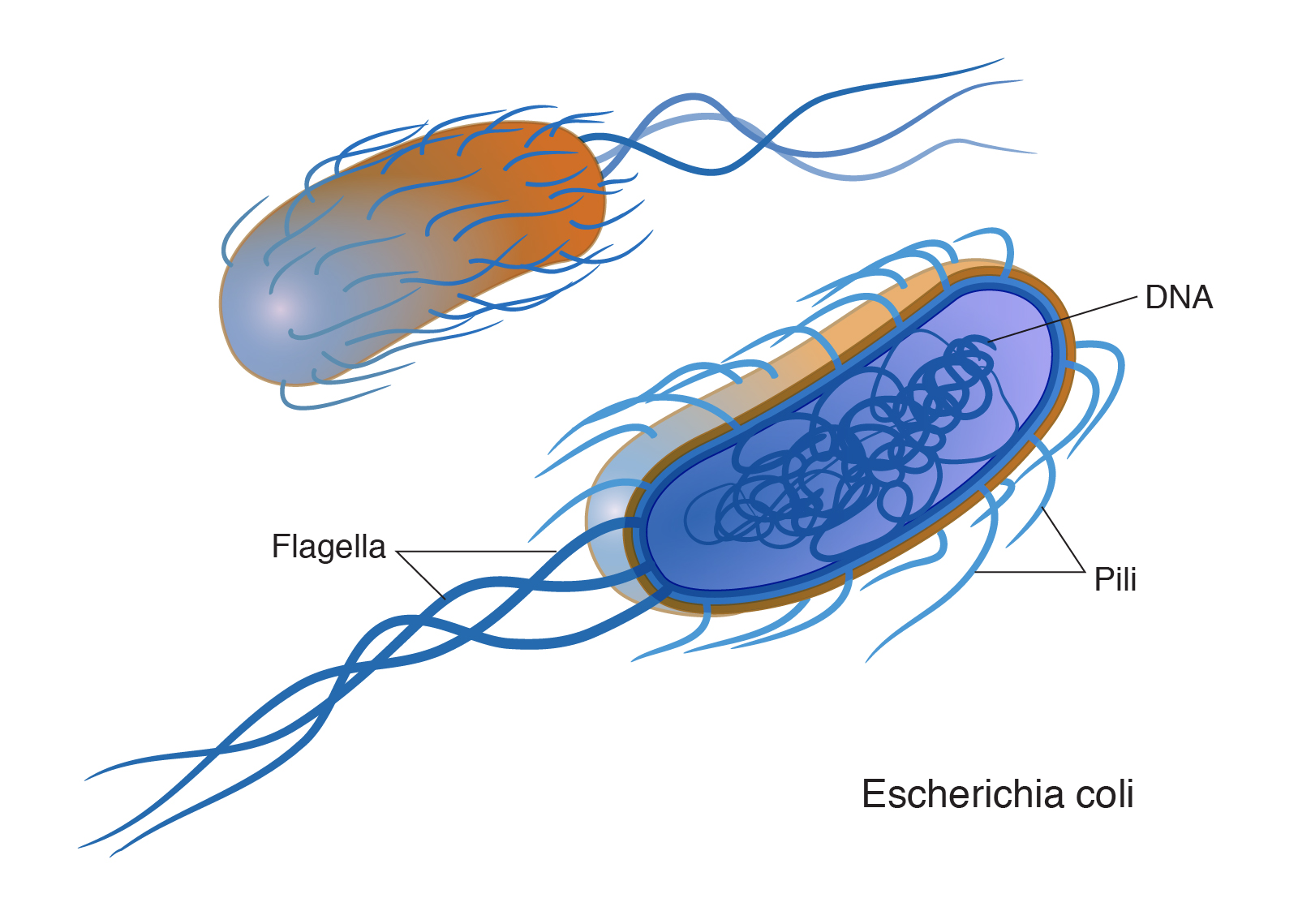 Bacteria are small single-celled organisms. Bacteria are found almost everywhere on Earth and are vital to the planet's ecosystems. Some species can live under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure. The human body is full of bacteria, and in fact is estimated to contain more bacterial cells than human cells.
Bacteria are small single-celled organisms. Bacteria are found almost everywhere on Earth and are vital to the planet's ecosystems. Some species can live under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure. The human body is full of bacteria, and in fact is estimated to contain more bacterial cells than human cells.